INTRODUCTION
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is one of the most prevalent non-communicable disease in the world (Prakash, 2013). According to World Health Organization (WHO), diabetes mellitus is becoming pandemic worldwide (Akhter et al., 2011; MMWR, 1989). It has been projected that prevalence may increase up to 11.1 million by the year 2030 in Bangladesh (Akhter et al., 2011). In 2014 about 8.4 million people were suffering from diabetes in Bangladesh (Akhter et al., 2014). The chronic hyperglycemia in DM may be associated with long-term damage and dysfunction leading to failure of various organs, especially the eyes, kidneys, nervous system, heart and blood vessels are involved (Fayed et al., 2013).
Different studies showed that anemia was a common complication in patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus (Prakash, 2013). Anemia increases the risk of cardiovascular disease and vascular complications of diabetes (Singh et al., 2009). It also causes weakness, tiredness, inability to work, headache, fatigue, pallor, tachycardia and poor wound healing (Griffith, 2002). It varies with age, sex, altitude, smoking, and pregnancy status (MMWR, 1989). According to WHO blood hemoglobin (Hb) less than 13 gm ⁄ dl and 12 gm ⁄dl respectively for an adult male and female are diagnosed as anaemia (Priyadarshini et al., 2015). Often anemia is unrecognized or overlooked and not treated due to its vague symptoms (Pape, 2011).
The etiology of anemia in diabetes is multi-factorial (Singh et al., 2009; Griffith, 2002). Chronic infection, inflammation, nutritional deficiencies, autoimmune disease, drugs and hormonal changes may be responsible. Unhealthy food habit and life style are also important factor for causing anaemia (MMWR, 1989; Fayed et al., 2013; Singh et al., 2009; Pape, 2011).
Hemolysis is one of the important cause for anemia in diabetes which may be due to increased osmotic fragility of RBC (Prakash, 2013; Priyadarshini et al., 2015; Ebrahim et al., 2012; Moussa, 2007; Ibanga et al., 2005). Osmotic fragility determines the rate of hemolysis of erythrocyte (Priyadarshini et al., 2015). Several studies showed that osmotic fragility was increased in hyperglycemia. Prakash (2013) observed that osmotic fragility was increased in chronic diabetic patients among Indian population. He suggested that osmotic fragility has relation with the duration of diabetes (Prakash, 2013). In another study it was found that erythrocyte fragility was more in diabetic than non diabetic. It was supposed that reduced surface area-to volume ratio of RBC might result in decreased RBC deformability leading to increased destruction and anemia (Prakash, 2013; Lippi et al., 2012).
In several studies it was observed that abnormal erythrocyte membranes formation in hyperglycemia might be associated with increased RBC fragility leading to anemia. This might be due to increased glycosylation of membrane protein, alteration of Na+/K+ATPase and changes of intracellular Ca+ (Prakash, 2013; Ebrahim et al., 2012; Moussa, 2007).
According to WHO prevalence of diabetes has risen faster in low and middle-income countries (Lippi et al., 2012; Imam, 2012; Chowdhury et al., 2015). Diabetes in Bangladeshi population is increasing year by year and becoming a major public health issue (Lippi et al., 2012). In diabetic patients, anemia is a common complication which is not known to the majority of people of Bangladesh (WHO, 2016). Though there are several studies in different countries but few scientific studies are available in our country regarding osmotic fragility status of red blood cell in type 2 diabetic patient. Considering the scarcity of studies in the literature the present study hopes to shed more light on the causes of hemolysis in Diabetes.
METHODS
This case control comparative study was conducted in Department of Physiology, Chittagong Medical College Hospital during January 2015 to December 2015. For this 200 subjects of both sexes with age range 30 – 70 years were included. The subjects were divided into 2 groups. Group A consisted of 100 newly diagnosed type 2 DM and Group B consisted of 100 age, sex, and BMI matched healthy subjects as control. The subjects with history of smoking and pregnancy, DM with systemic diseases like HTN, IHD, CVD, COPD, CKD, liver diseases and thyroid disorder, hemolytic disorders, bleeding disorder, collagen disease, autoimmune disease, drugs which causes hemolysis were excluded from this study. The protocol of this study was approved by ethical review committee of Chittagong Medical College.
All subjects were selected purposively on the basis of their attending in outpatient department at Chittagong Diabetic Hospital for treatment and follow up with history of diabetes without any known complication during time period 8.30 to 11am. Age, sex and BMI matched non diabetic attendants and staffs of Chittagong Medical College Hospital and Chittagong Diabetic Hospital were taken as control.
After selection and proper counseling, the aim, objectives and the procedure of the study was explained in details to all subjects. The subjects were allowed to withdraw themselves from the study if they like. An informed written consent was taken from all the subjects included in the study and detailed personal information, medical and family history was recorded in a preformed questionnaires. Height in cm and weight in kg were measured, BMI was calculated (weight in kilogram divided by height in square meter). Pulse, blood pressure were recorded (aneroid sphygmomanometer). Anemia, jaundice, edema were observed in all study groups and controls.
FBS, 2HPPBS, Hb level, serum creatinine and SGPT and SGOT and fasting lipid profile of all control subjects were done to exclude diabetes, kidney failure, anemia and liver disfunction. All these tests were also done in type 2 DM to exclude these abnormalities. In diabetic patients blood glucose and Hb were measured to observe the glycemic status and anaemia in these patients.
With all aseptic precaution about 7 ml of venous blood was drawn from medial cubital vein with the using spirit and disposable syringe for each individual. One ml was collected in an anticoagulant (potassium oxalate) containing test tube vacuette (greiner bio-one) for osmotic fragility test. 2 ml for Hb and HbAlc estimation in Lavender tube (greiner bio-one), 2 ml for FBS and 2HPPBS in Glucose tube or Gray tube (greiner bio-one) and rest of the 2 ml for Lipid profile, Serum creatinine, SGPT and SGOT in Red tube (greiner bio-one).
Hb estimation, HbAlc percentage, FBS, 2HPPBS, Fasting Lipid Profile, Serum creatinine, SGPT and SGOT level were measured by auto analyzer machine (dimension expand plus, made in UK).
Osmotic fragility was measured by traditional method. For performing the fragility test of RBC, a series of hypotonic solution of NaCl were made with different strength in twelve test tubes, numbered serially (no-1 was 0.9% of NaCl to no-12 was 00%) and kept in the test tube rack. One drop of anticoagulant mixed blood was added in each test tube, mixed gently by inverting the test tubes. After waiting for about half an hour for hemolysis, the test tubes were centrifuged for about 5 minutes at 2000 RPM (deluxe model). After centrifuging, the test tubes were kept in the rack and the stage of hemolysis was observed and recorded in data sheet.
Data were processed and analyzed using computer based software SPSS (Statistical package for social sciences) for windows version 20. Unpaired t-test was used to compare quantitative variables. Variables were expressed as mean ± SD and range. p value < 0.05 were considered as significant.
RESULTS
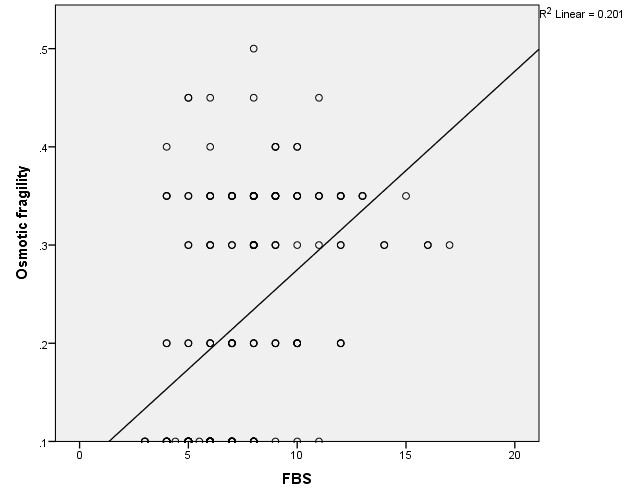
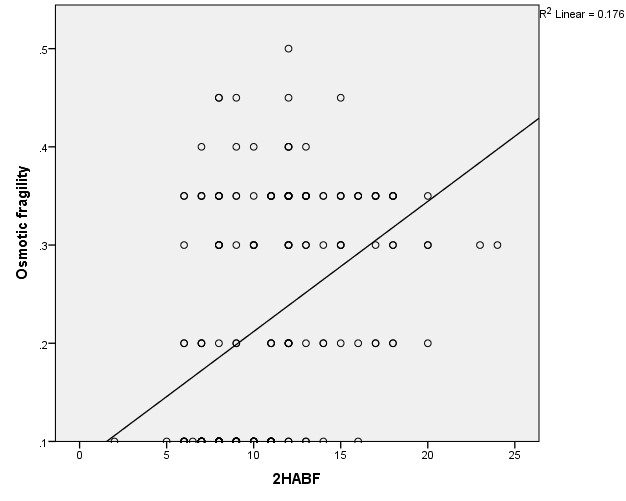
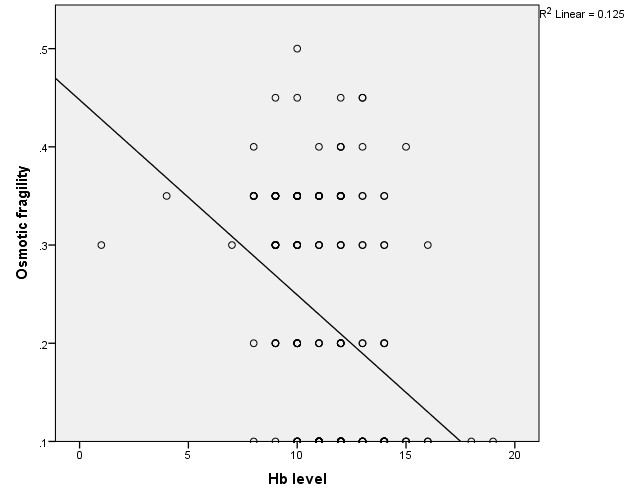
Mean (±SD) Hb gm/dl were significantly lower (<0.05) in group A (study group) (10.11 ± 1.18) gm/dl than group B (control group) (12.75 ± 2.09) gm/dl. Mean (±SD) HbA1c %, were significantly higher (<0.001) in group A (9.12 ± 3.80)% than group B (4.58 ± 2.22)% (Table 1). Mean value of NaCl solution for partial and complete hemolysis in group A were 0.44 ± 0.06%, 0.32 ± 0.02%. In group B it was 0.40 ± 0.05% and 0.30 ± 0.03% respectively. No significant difference (p value > 0.05) was observed between two groups regarding partial and complete hemolysis of RBC (Table 2). Normal hemolysis was 87% in group A and 12% had early hemolysis and 1% had late hemolysis. 100% normal hemolysis were observed in group B (Table 3). On correlation analysis FBS and 2 HPPBS showed significant (p<0.001) positive correlation with osmotic fragility (Figure 1 and Figure 2). Hb level showed significant (p<0.001) negative correlation with osmotic fragility (Figure 3 and Table 4).
Table 1. Hemoglobin level of study groups
| Hemoglobin level(gm/dl) |
10.11 ± 1.18
(8-14) |
12.75 ± 2.09
(11-18) |
<0.05* |
| HbA1c (%) |
9.12 ± 3.80
(6-11) |
4.58 ± 2.22
(3-6) |
<0.001*** |
Values are expressed as mean ±SD, p values were obtained by unpaired Students ‘t’ test. Group A: Type 2 diabetic patients. Group B: Non diabetic healthy subjects. Values in parenthesis indicate range. n = number of subjects. * marks signify significance of test. |
Table 2. Hemolysis of RBC in different concentration of NaCl solution in study groups (n=200)
| Partial hemolysis |
0.44 ± 0.06
(0.38-0.50) |
0.40 ± 0.05
(0.41-0.45) |
>0.05 |
| Complete hemolysis |
0.32 ± 0.02
(0.30-0.34) |
0.30 ± 0.03
(0.30-0.33) |
>0.05 |
Values are expressed as mean ±SD. p values were obtained by unpaired Students ‘t’ test. Group A: Type 2 diabetic patients. Group B: Non diabetic healthy subjects.
Values in parenthesis indicate range. n = number of subjects. |
Table 3. Nature of hemolysis in the study groups (n= 200)
|
No. |
(%) |
No. |
(%) |
| Normal hemolysis |
87 |
87% |
100 |
100% |
| Early hemolysis |
12 |
12% |
0 |
0% |
| Late hemolysis |
1 |
1% |
0 |
0% |
n = number of subjects |
Table 4. Correlation between osmotic fragility (OF) with Hb level, FBS, 2HPPBS of cases. (n=100)
|
r value |
P value |
| Hb |
-0.362 |
<0.001* |
| FBS |
0.480 |
<0.001* |
| 2HPPBS |
0.443 |
<0.001* |
Pearson’s correlation- coefficient(r) test was performed as the test of significance.
OF- osmotic fragility.FBS- fasting blood sugar. 2 HPPBS- two hours post prandial blood sugar. * marks signify significance of test. |
DISCUSSION
Test of Osmotic fragility Status of RBC is a simple and easy assessment reflecting altered membrane physiology (Prakash, 2013; Priyadarshini et al., 2015; Ebrahim et al., 2012) and is the determinant of stability and strength of RBC in different osmotic gradient (Abate et al., 2013). Hemolysis usually starts at 0.45% - 0.05% & it completes at 0.3% - 0.33% solution of NaCl. In our study 87% of study group (group A) showed normal hemolysis. Only 12% study group showed early hemolysis. Mean value of NaCl solution for partial and complete hemolysis in study group (group A) were 0.44 ± 0.06%, 0.32 ± 0.02%. In control (group B) it was 0.40 ± 0.05% and 0.30 ± 0.03% respectively. No significant difference was observed between study group (group A) and control (group B) regarding partial and complete hemolysis of RBC (p value < 0.05). Some previous studies RBC osmotic fragility was increased in diabetic patients (Prakash, 2013; Singh et al., 2009; Pape, 2011; Ebrahim et al., 2012; Ibanga et al., 2005; Tomas et al., 2003). In a study conducted by Prakash (2013) showed significant increased hemolysis of diabetic patients sufferings from more than 5 years and less than 5 years. Our findings simulates with the previous study.
In our study there was significant reduction of hemoglobin comparing to control group (p <0.05). In some previous study most of the diabetic patients were found anaemic (Akhter et al., 2011; Fayed et al., 2013; Singh et al., 2009; Griffith, 2002; Tomas et al., 2003). Altered RBC membrane physiology in DM patients may result in increased hemolysis, leading to anemia though other factors are also responsible (Prakash, 2013; Ebrahim et al., 2012; Moussa, 2007).
In our study RBC osmotic fragility status was not significantly increased in either type of hemolysis. Probably the cause may due to less duration of sufferings from diabetes. Our findings dissimilar with other studies (Prakash, 2013; Akhter et al., 2011; Fayed et al., 2013; Singh et al., 2009; Ibanga et al., 2005), may be the duration were longer in their cases (Priyadarshini et al., 2015). In our study the effects of age, food habit, environmental factor and nutrient supplement may make RBC more resistant to hemolysis in hypotonic solution. Our sample size is small, all diabetic groups were newly diagnosed and history of diabetes was less than 3 years.
In our study we found negative correlation between osmotic fragility of RBC with hemoglobin which simulates with other studies (Prakash, 2013; Fayed et al., 2013; Priyadarshini et al., 2015).
There were moderate positive correlation was seen between osmotic fragility and blood sugar (FBS and 2HPPBS) which simulates with Lippe et.al (Priyadarshini et al., 2015).
Cause of anaemia in diabetic patients is multifactorial (Fayed et al., 2013). One of the proposed mechanism is abnormality of RBC membranes due to chronic exposure in a hyperglycemic environment (Prakash, 2013; Moussa, 2007; Ibanga et al., 2005). It has been suggested that RBC membrane abnormality in diabetic environment may be due to factors like (a) increased glycosylation of hemoglobin and membrane protein (Prakash, 2013; Mahtab, 2003; Bogdanva et al., 2013; Balasubramanyam, 2003; Jha and Rizvi, 2011), (b) imbalance between Na+, K+ and ATPase (Lippi et al., 2012), (c) accumulation of free radicals due to oxidative stress (Pape, 2011; Ibanga et al., 2005; Balasubramanyam, 2003; Tomas et al., 2003), (d) lipid peroxidation (Balasubramanyam, 2003; Jha and Rizvi, 2011), and (e) decreased Ca+ homeostasis (Moussa, 2007) etc. All of these processes result in lysis of RBC leading to increased osmotic fragility and anaemia. The osmotic effects of hyperglycemia and glycosylation of hemoglobin and erythrocyte membrane protein may play important role in decreased deformability of RBC (Prakash, 2013; Moussa, 2007; Ibanga et al., 2005). These changes may be responsible for microcirculatory dysfunction in patients in poorly controlled DM (Prakash, 2013; Fayed et al., 2013; Pape, 2011; Lippi et al., 2012).
CONCLUSION
The results of this study indicate that osmotic fragility of RBC though in small percentage may be increased in type II diabetes mellitus. Further research work to see the rheological changes can be done with large sample size with longer duration in controlled and uncontrolled diabetic patients.

 Full Text (PDF)
Full Text (PDF)